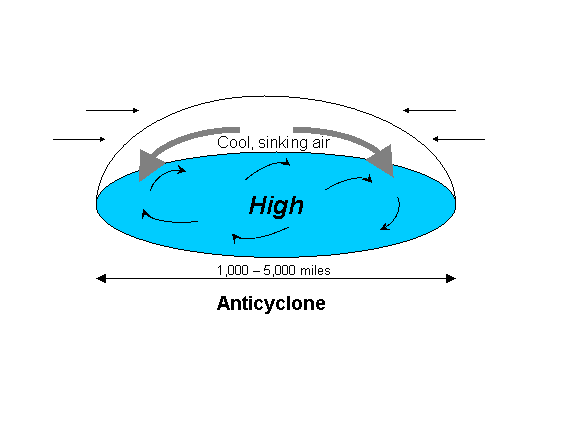
An anti-cyclone -- also known as a high pressure area -- is a large atmospheric circulation system with the wind flowing clockwise
around it in the Northern Hemisphere, and counter-clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
Anticyclones form from air masses cooling more than their surroundings, which causes the air to contract slightly making the air more dense. Since dense air weighs more, the weight of the atmosphere overlying a locatiion increases, causing increased surface air pressure.
The air mass cooling that results in an anticyclone forming can be caused by either conduction as the air flows over a relatively cool ocean surface, or through the loss of infrared radiation over
land during the fall, winter, or spring when little sunlight is available to warm the air mass.
|