

|
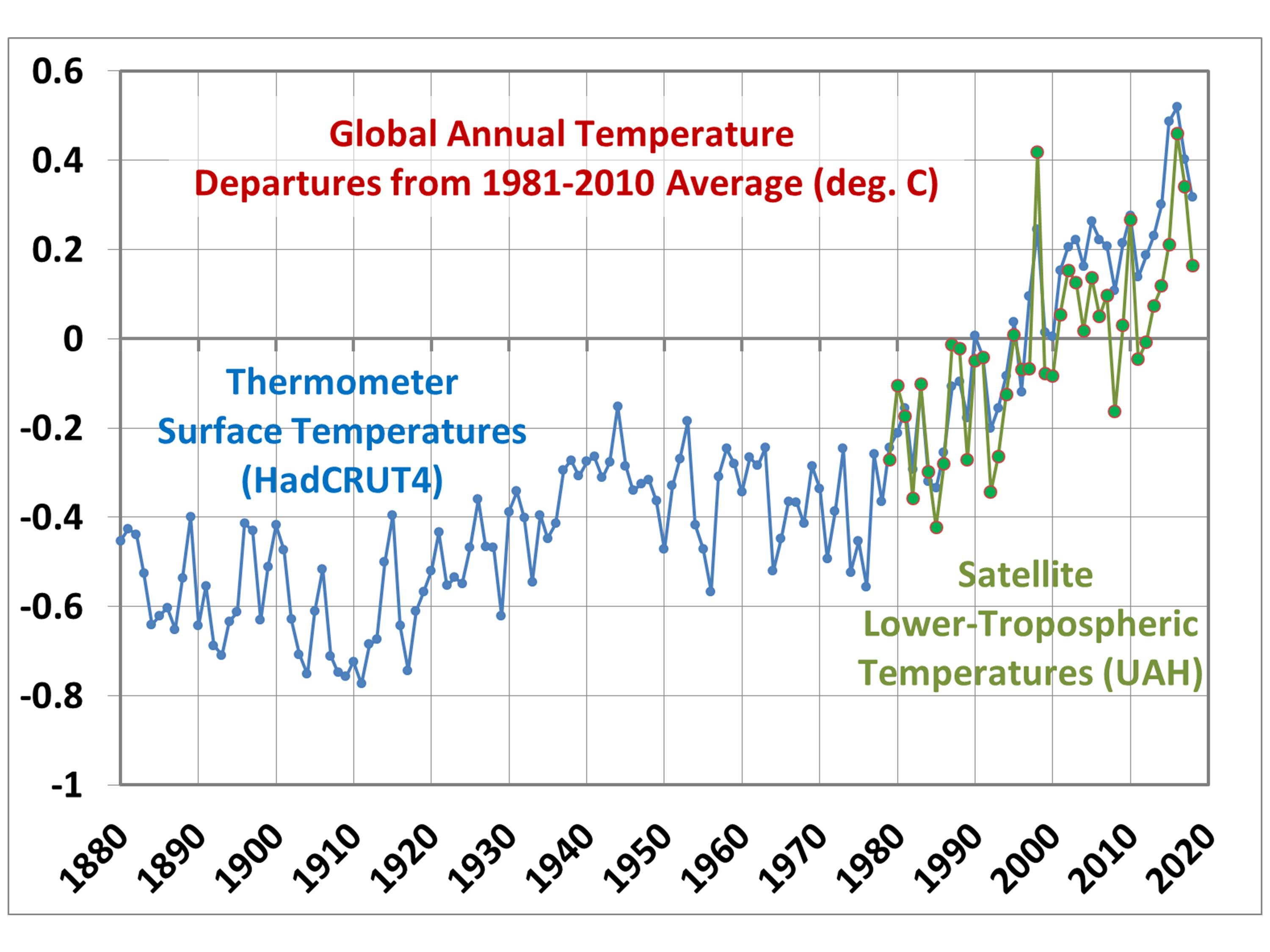
|
What causes global warming? |
| 'Global warming' refers to the gradual warming of global-average temperatures observed over the last 50 years or more. While the term has
been popularized to imply a human cause of the warming, there are also theories regarding potential natural causes. While media reports usually imply recent warming
is entirely caused by human activities, the consensus of scientific opinion as summarized by the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
states only that 'most' (more than half) of warming since the 1950s is likely due to humans. There is no way to know the exact proportion, though, because
the imbalance in global energy flows associated with the warming of the upper 2,000 meters of the global oceans since the early 1990s
is smaller than our knowledge of those energy flows (either from global observations, or from first physical principles). As a result, recent warming could have a
large natural component and we would not know it.
On time scales of years or longer, global surface air temperatures (or lower atmospheric temperatures) can rise (or fall) from two main process: (1) a change in in the radiative energy balance of the Earth, or (2) a change in the rate of overturning of the oceans. The radiative balance of the Earth is between the rates of absorbed solar radiation which heats the Earth, and loss of infrared (IR) radiation to space which cools the Earth. The most popular explanation of global warming is that anthropogenic (human-caused) greenhouse gas emissions (mostly carbon dioxide from fossil fuel burning) are reducing the Earth's ability to cool to outer space through infrared radiation. But any process which alters the the amount of absorbed sunlight or emitted IR radiation can cause global warming. For example, changing circulation patterns of the coupled ocean-atmosphere system can cause changes in cloud cover, which can change the amount of sunlight which reaches the surface. There is also a theory than changes in solar activity cause variations in how many cosmic rays enter Earth's atmosphere, which are believed to have an effect on cloud formation. These theories of natural climate change have less support, though, partly because there is not as much data to explore them. In the case of the carbon dioxide theory, in contrast, there are accurate long term measurements as well as extensive laboratory evidence of the effect of CO2 on infrared radiative transfer in the atmosphere. So, our theories of natural climate change are not nearly as well developed as the theory of anthropogenic climate change. Also poorly understood are potential long-term changes in the overturning of the global oceans. Because most of the world's oceans below a depth of a few hundred feet are quite cold, a change in the rate of overturning can cause warming or cooling. For example, the climate system warms up during El Nino years, when the rate of upwelling of cold ocean water in the tropical east Pacific is reduced. Since El Ninos were more prevalent between the 1970s and 2000, which was also the period of most rapid temperature rise, it is possible that more El Ninos caused some unknown fraction of the warming. But since very little government sponsored research goes into studing natural sources of climate change, the anthropogenic theory is currently dominant. |
| (page last updated 1/19/2022) |
| SELECT BOX EXAMPLES: | ||
|
||
| Copyright © 2023 WeatherStreet.com |
| Put our free WeatherStreet weather lookup on your web page. |
Terms & Conditions

|
|
|